Tooth infections, also known as dental abscesses, are a common dental problem that can cause significant pain and discomfort. These infections occur when bacteria invade the tooth and cause an accumulation of pus in or around the root. Anyone, from children to the elderly, can develop a tooth infection. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of a tooth infection to seek prompt dental care and prevent further complications.
In this blog, we will discuss the key highlights of tooth infections, including the causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options. We will also provide information on how to prevent tooth infections through good oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups. By understanding the signs of a tooth infection and taking appropriate action, you can protect your oral health and overall well-being.
Understanding Tooth Infections
A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, is a bacterial infection that occurs in or around the root of a tooth. It is characterized by the formation of a pocket of pus, which can cause pain, swelling, and other symptoms. The infection is typically caused by bacteria that enter the tooth through a deep cavity, a cracked tooth, or gum disease. If left untreated, a tooth infection can spread to other parts of the body and lead to serious complications.
What Constitutes a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, or a dental abscess, is characterized by the presence of a pocket of pus in or around the root of a tooth. This pocket of pus is formed as a result of a bacterial infection. The bacteria enter the tooth through a cavity, a crack in the tooth, or gum disease. Once inside the tooth, the bacteria multiply and cause an inflammatory response, leading to the formation of pus. The pocket of pus can cause pain, swelling, and other symptoms. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other areas of the body and lead to serious complications. It is important to seek dental care if you suspect a tooth infection to prevent further complications.
Common Causes of Tooth Infections
There are several common causes of tooth infections. The most common cause is dental decay, which occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the tooth enamel and create cavities. If these cavities are left untreated, the bacteria can penetrate the inner layers of the tooth and cause an infection.
A weakened immune system can also increase the risk of developing a tooth infection. Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, and cancer can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is another common cause of tooth infections. Gum disease occurs when bacteria build up in the gums and cause inflammation and infection. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and increase the risk of developing a tooth infection.
By practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly, and seeking prompt treatment for dental decay and gum disease, you can reduce your risk of developing a tooth infection.
Early Signs of Tooth Infection
Recognizing the early signs of a tooth infection is crucial for seeking prompt dental care and preventing further complications. One of the most common early signs is a toothache, which can range from a dull ache to a sharp, throbbing pain. Swelling around the affected tooth or in the surrounding gums is another common sign of a tooth infection. The presence of pus, which may appear as a white or yellowish discharge, is also indicative of an infection. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
Pain and Discomfort: Not Just an Ordinary Toothache
While toothaches are a common dental problem, they can also be a sign of a more serious issue, such as a tooth infection. A tooth infection, also known as an abscessed tooth, occurs when bacteria invade the innermost part of the tooth, known as the pulp. The bacteria cause an infection, leading to inflammation and the formation of pus. This can result in severe pain and discomfort in the affected tooth. It is important to seek dental care if you experience persistent or severe tooth pain, as it may be a sign of an abscessed tooth. Your dentist can evaluate the tooth and recommend appropriate treatment, such as a root canal or extraction, to alleviate the pain and treat the infection at its source.
Sensitivity to Hot and Cold Foods
Sensitivity to hot and cold foods is another common symptom of a tooth infection. The infection can cause the tooth’s enamel to erode, exposing the sensitive underlying layers of the tooth. As a result, you may experience discomfort or pain when consuming hot or cold foods and beverages.
This sensitivity is often a sign that the infection has spread to the nerves and blood vessels within the tooth. It is important to seek dental treatment if you experience sensitivity to hot and cold foods, as it may indicate an underlying tooth infection. Your dentist can evaluate the tooth and recommend appropriate treatment, such as a root canal or extraction, to address the infection and alleviate the sensitivity.
Advanced Symptoms of Tooth Infection
While early signs of a tooth infection can be uncomfortable, advanced symptoms can be more severe and may require immediate medical attention. In some cases, a tooth infection can lead to difficulty breathing due to swelling in the face or neck. This can indicate that the infection has spread beyond the tooth and may be affecting the airway.
Another advanced symptom of a tooth infection is the enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck or jaw. Lymph nodes are part of the body’s immune system and can become swollen and tender in response to an infection.
If you experience either of these advanced symptoms, it is important to seek emergency medical care. Untreated tooth infections can lead to serious complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Swelling in the Face or Cheek
Swelling in the face or cheek is an advanced symptom of a tooth infection that requires immediate medical attention. This swelling occurs when the infection spreads beyond the tooth and affects the surrounding tissues and structures. The swelling may be localized to the area around the infected tooth or may spread to other areas of the face and head.
In some cases, the infection can even affect the sinus cavity, leading to sinusitis. The sinuses are air-filled cavities located in the bones of the face and skull. When the infection spreads to the sinus cavity, it can cause pain, pressure, and congestion.
If you experience swelling in the face or cheek, it is important to seek emergency dental care. Untreated tooth infections can lead to serious complications, including the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Pus or Discharge from the Infected Tooth
Pus or discharge from the infected tooth is a sign that the abscess, or pocket of pus, has ruptured. The discharge may appear as a thick, yellowish fluid and may have a foul odor. The presence of pus indicates that the infection has spread and is draining from the tooth.
It is important to seek dental care if you notice pus or discharge from an infected tooth. The pus is a sign that the infection is active and needs to be treated. Your dentist can evaluate the tooth and recommend appropriate treatment, such as a root canal or extraction, to address the infection and prevent further complications.
When to Seek Dental Care
Knowing when to seek dental care for a tooth infection is important for preventing complications and ensuring prompt treatment. If you experience severe pain, swelling, or difficulty breathing, it is important to seek emergency medical care. These symptoms can indicate that the infection has spread and requires immediate attention.
In general, you should seek dental care if you experience persistent or severe tooth pain, swelling, or other symptoms of a tooth infection. Your dentist can evaluate the tooth and recommend appropriate treatment, such as a root canal or extraction, to address the infection and alleviate your symptoms.
Fever and General Malaise: Signs of Spreading Infection
Fever and general malaise, or a feeling of unwellness, are signs that a tooth infection may be spreading and affecting other areas of the body. Fever is the body’s natural response to infection and is characterized by an elevated body temperature. General malaise may include symptoms such as fatigue, muscle aches, and a general sense of discomfort.
In addition to fever and malaise, swollen lymph nodes may also be present. Lymph nodes are part of the body’s immune system and can become enlarged and tender in response to an infection.
If you experience fever, general malaise, or swollen lymph nodes along with symptoms of a tooth infection, it is important to seek dental care. These symptoms may indicate that the infection has spread and requires immediate treatment to prevent further complications.
Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: Emergency Warning Signs
Difficulty breathing or swallowing are emergency warning signs of a tooth infection and require immediate medical attention. These symptoms indicate that the infection has spread and is affecting the airway. In severe cases, a tooth infection can lead to airway obstruction, which can be life-threatening.
If you experience difficulty breathing or swallowing along with symptoms of a tooth infection, such as severe pain, swelling, or fever, it is important to seek emergency medical care. Call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room for immediate treatment.
In the meantime, you can take over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to help manage the pain. However, these medications will not treat the underlying infection and should not be used as a substitute for dental care.
|
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection Requiring Emergency Medical Attention |
|
Difficulty breathing |
|
Difficulty swallowing |
|
Severe pain |
|
Swelling in the face or neck |
|
Fever |
|
General malaise |
|
Swollen lymph nodes |
|
Trouble breathing or swallowing are emergency warning signs of a tooth infection and require immediate medical attention. |
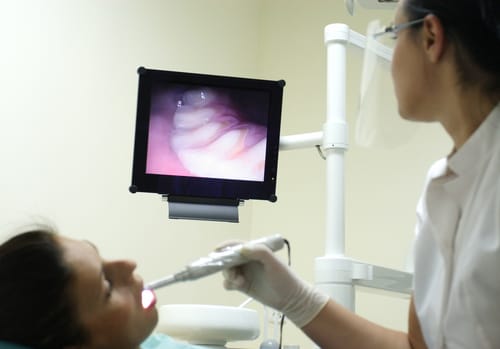
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing a tooth infection involves a combination of dental x-rays, CT scans, and physical examinations. These diagnostic approaches help the dentist identify the location and extent of the infection and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Dental X-rays are commonly used to visualize the tooth and surrounding structures. They can reveal signs of tooth decay, abscesses, and other dental abnormalities. CT scans may be used in more complex cases to provide a detailed, three-dimensional image of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding tissues.
In addition to imaging studies, a physical examination of the tooth and surrounding gums is conducted to assess for signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, or discharge. By combining these diagnostic approaches, dentists can accurately diagnose tooth infections and develop an effective treatment plan.
Dental X-rays: Revealing the Hidden
Dental X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing tooth infections. They can reveal hidden dental problems, such as tooth decay, that may not be visible to the naked eye. X-rays allow dentists to see the internal structures of the teeth, including the root and surrounding bone.
In the case of a tooth infection, dental X-rays can show signs of tooth decay, abscesses, and other abnormalities. These images help dentists determine the location and extent of the infection and guide treatment decisions. For example, if a tooth infection has spread to the surrounding bone, a dental X-ray can show the extent of the bone loss and help the dentist determine the appropriate treatment approach, such as a root canal or extraction.
Dental X-rays are a valuable diagnostic tool that allows dentists to accurately assess the presence and severity of tooth infections, leading to effective treatment and improved oral health.
Physical Examination: Looking Beyond the Surface
In addition to dental X-rays and imaging studies, a physical examination of the tooth and surrounding gums is an important part of diagnosing tooth infections. During the examination, the dentist will assess for signs of inflammation, such as swelling, redness, or tenderness.
The dentist will also look for specific signs of a tooth infection, such as the presence of a dental abscess or periodontal abscess. A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus that forms within the tooth or the surrounding tissues. A periodontal abscess, on the other hand, occurs in the gums and often resembles a pimple.
By conducting a thorough physical examination, the dentist can gather important information about the location and severity of the infection, which will guide the treatment plan. This comprehensive approach to diagnosis ensures that all aspects of the tooth infection are taken into account and appropriate treatment is provided.
Treatment Options for Tooth Infection
The treatment options for a tooth infection depend on the severity and location of the infection. In many cases, a root canal treatment is the preferred approach. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth, cleaning the root canals, and sealing them to prevent further infection. A crown or filling is then placed on the tooth to restore its function and appearance.
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control the infection. Antibiotics are typically used in conjunction with other dental treatments, such as a root canal or extraction.
In severe cases, extraction of the infected tooth may be necessary. This is usually a last resort when other treatment options have been exhausted or when the infection has caused significant damage to the tooth or surrounding structures.
Your dentist will evaluate your specific case and recommend the most appropriate treatment option to address the tooth infection and alleviate your symptoms.
Root Canal: A Common Solution
A root canal treatment is a common solution for treating tooth infections. It involves removing the infected pulp from the innermost part of the tooth, known as the root canal. The root canals are then cleaned and disinfected to remove any remaining bacteria. Once the infection is cleared, the canals are filled and sealed to prevent further infection.
A root canal treatment is typically performed under local anesthesia to ensure your comfort during the procedure. After the root canal, a crown or filling is placed on the tooth to restore its strength and function.
Root canal treatments are highly successful in saving infected teeth and relieving toothache pain. By preserving the natural tooth, a root canal can prevent the need for extraction and maintain the aesthetics and function of your smile.
Antibiotics: Fighting the Infection
Antibiotics may be prescribed to fight the bacterial infection associated with a tooth infection. They are typically used in cases where the infection has spread beyond the tooth and is affecting other areas of the body or when there is a risk of complications.
The goals of antibiotic treatment for a tooth infection are to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection, reduce inflammation and pain, and prevent the spread of infection. Antibiotics work by targeting and killing the bacteria responsible for the infection.
It is important to note that antibiotics alone are not a sufficient treatment for a tooth infection. They should be used in conjunction with other dental treatments, such as a root canal or extraction, to fully address the infection. Your dentist will determine the most appropriate antibiotic and treatment plan based on the severity and location of the infection.
Can Tooth Infections Heal on Their Own?
Tooth infections cannot heal on their own. They require prompt dental care to eliminate the infection and prevent further complications. Even if symptoms temporarily improve, the infection can still be present and may require treatment to fully resolve.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing tooth infections begins with practicing good oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help remove bacteria and plaque that can lead to tooth decay and gum disease. It is also important to limit sugary foods and drinks, as they contribute to tooth decay.
Regular dental check-ups are essential for preventing tooth infections. Your dentist can identify and treat dental problems, such as cavities or gum disease before they progress to an infection. Prompt treatment of dental decay, such as fillings or root canal treatment, can help prevent the spread of infection to the tooth’s root.
By adopting these prevention strategies and maintaining good oral health habits, you can reduce your risk of developing a tooth infection and protect your overall oral health.
Regular Dental Check-ups: A Must
Regular dental check-ups are vital for maintaining good oral health and preventing tooth infections. During these check-ups, your dentist will examine your teeth and gums for signs of cavities, gum disease, and other dental problems. They can also perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup, which can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
By scheduling regular dental check-ups, usually every six months, you can catch dental problems early and prevent them from progressing to a tooth infection. Your dentist can provide personalized recommendations based on your oral health needs, such as additional cleanings or preventive treatments.
In addition to regular check-ups, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist if you experience any signs or symptoms of a tooth infection, such as toothache, swelling, or discharge. Prompt dental care can prevent further complications and preserve your oral health.
Good Oral Hygiene Practices: Your First Defense
Good oral hygiene practices are your first line of defense against tooth infections. By practicing proper oral hygiene, you can remove plaque and bacteria that can lead to tooth decay and gum disease. Here are some important practices to include in your daily oral hygiene routine:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes each time. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to effectively clean your teeth and remove plaque.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. Use a gentle sawing motion and be sure to clean both sides of each tooth.
- Use mouthwash to rinse your mouth and kill bacteria. Look for a mouthwash that contains fluoride and has been approved by your dentist.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles become frayed. A worn toothbrush is less effective at removing plaque and bacteria.
- Maintain a healthy diet that is low in sugar and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit your intake of sugary snacks and drinks, as they can contribute to tooth decay.
By following these good oral hygiene practices, you can reduce your risk of developing a tooth infection and maintain a healthy smile.
Contact Dentistry Of West Bend For An Appointment
Recognizing the signs of a tooth infection is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. From early indicators like pain and sensitivity to advanced symptoms such as swelling and discharge, understanding these signs can prevent further complications. Seeking dental care promptly when experiencing symptoms like fever or difficulty breathing is essential to prevent the infection from spreading. Remember, regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are key prevention strategies. Prioritize your oral health to maintain a healthy and infection-free smile. If you have any concerns or questions about tooth infections, don’t hesitate to consult with us for expert advice and guidance.

Recent Comments