Periodontal disease is a severe gum infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone that supports your teeth. Left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems. We will start with understanding what it is, how it progresses from gingivitis to periodontitis, and its causes and symptoms. We will then move on to diagnosis and treatment options, including non-surgical treatments, surgical treatments for advanced periodontal disease, and prevention strategies such as home care tips and regular dental visits. Lastly, we will discuss how to manage periodontal disease at home and when to consult a dentist for proper treatment.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a condition that affects the gum tissue and can eventually lead to tooth loss. Plaque buildup, caused by bacteria in the mouth, is a significant factor in the development of periodontal disease. By practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as regular brushing and flossing, and visiting a dental hygienist for professional cleanings, you can help prevent periodontal disease. Inflammation of the gums is a common symptom, and poor oral hygiene habits increase the risk of developing this form of gum disease.
The Progression from Gingivitis to Periodontitis
Gingivitis is the early stage of periodontal disease, which can progress to periodontitis if left untreated. Periodontitis involves the infection and inflammation of the gums caused by the toxins released by bacteria in plaque. Treating gingivitis promptly is crucial to prevent its progression to periodontitis. Understanding the progression from gingivitis to periodontitis is essential to ensure timely intervention and prevent further complications. By addressing gingivitis early on, individuals can effectively manage their oral health and avoid the more severe form of gum disease.
Causes and Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
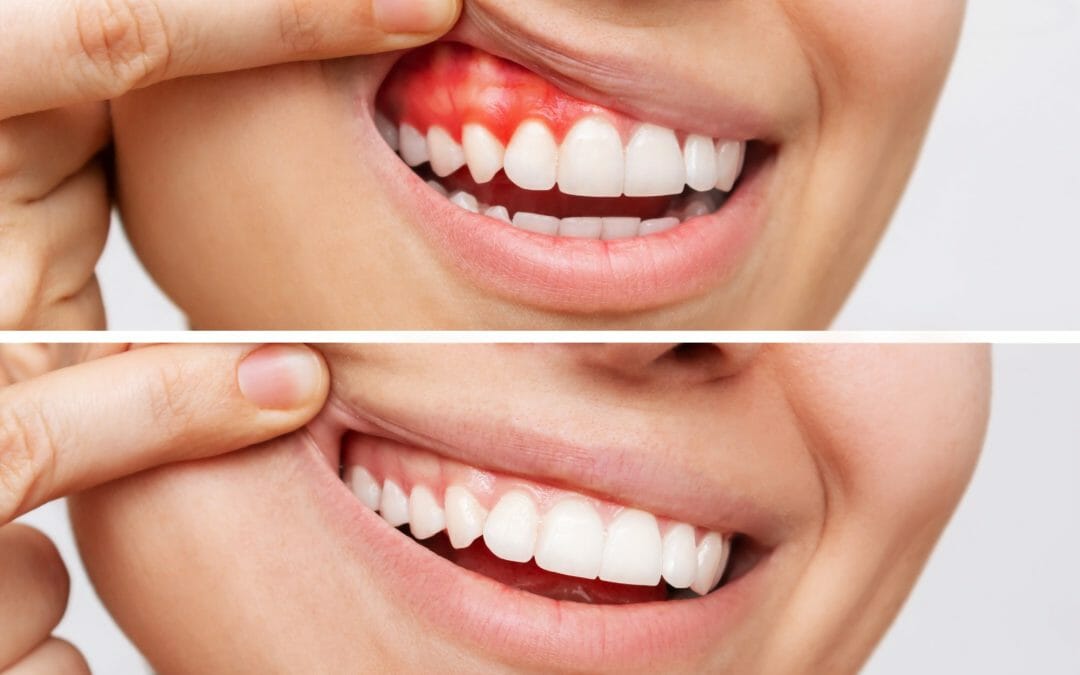
Poor oral hygiene is a common cause of periodontal disease. Smoking increases the risk of developing this condition. Symptoms include red, swollen, or bleeding gums and bad breath. Hormonal changes can also contribute to its development. It’s important to note that periodontal disease can severely affect overall health. Regular visits to a periodontist or hygienist are crucial for prevention and early detection. Maintaining good oral care habits, such as daily brushing and professional cleanings, can help prevent discomfort and complications associated with periodontal disease.
Diagnosis of Periodontal Disease
Dentists employ various techniques to diagnose periodontal disease. Through a clinical examination, they check for gum inflammation and recession, indicating the disease’s presence. X-rays detect bone loss caused by periodontal disease, providing a clearer picture of its severity. Another method involves measuring pocket depth, which helps assess the extent of the disease. Additionally, dentists may use a probe to evaluate the firmness of the gum tissue, providing further insight into the condition of the gums.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
Non-surgical treatments, such as scaling and root planing, are commonly used as the initial approach to combat periodontal disease. Removing plaque and tartar below the gum line helps address the condition’s underlying cause. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to treat any bacterial infections associated with periodontal disease. However, in more advanced cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. Flap surgery, for instance, enables deep cleaning of the root surfaces and removing infected tissue. Periodontists and dental hygienists can effectively manage this gum disease by exploring these treatment options.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Their Effectiveness
Non-surgical treatments play a significant role in the effective management of periodontal disease. Scaling and root planing are standard procedures that remove plaque and tartar from the root surfaces, promoting gum health. Antibiotics can be prescribed to control bacterial infections in the gums. Regular dental cleanings and proper oral hygiene education help prevent the progression of periodontal disease. Laser therapy is another non-surgical option that targets infected tissue and supports healing.
Surgical Treatments for Advanced Periodontal Disease
In cases of advanced periodontal disease, surgical treatments may be necessary to restore oral health. Flap surgery is performed to access the root surfaces for thoroughly cleaning and removing infected tissue. In some instances, bone grafting may be required to replace lost bone. Guided tissue regeneration is an option that promotes the regeneration of gum tissue and bone.
Is Periodontal Disease Curable?
Periodontal disease can be managed with early detection and treatment. Professional dental care and good oral hygiene are essential in controlling its progression. Regular dental check-ups help monitor the condition and prevent further damage. Treatment options, like scaling and root planing, remove plaque and tartar buildup.
Prevention Strategies
Regular brushing and flossing prevent gum disease by removing plaque buildup. Additionally, avoiding tobacco use reduces the risk of developing periodontal disease. A balanced diet, low in sugary foods, promotes oral health. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash helps reduce bacteria that can cause gingivitis. It is also important to schedule regular dental cleanings to remove plaque and tartar that brushing alone cannot eliminate.
Living with Periodontal Disease
Proper oral hygiene practices are essential for managing the symptoms of periodontal disease. Regular dental visits are crucial in monitoring and managing the condition effectively. Following the treatment plan your dentist recommends to maintain optimal oral health is vital. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and avoiding tobacco use, can also support gum health. Seeking professional help and support can significantly improve the quality of life while living with periodontal disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, periodontal disease is a severe dental condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. It is essential to understand the progression of the disease from gingivitis to periodontitis and identify the common symptoms. Regular dental visits and proper home care can help prevent the development and progression of periodontal disease. Non-surgical treatments such as scaling and root planing effectively treat milder cases, while surgical options may be necessary for advanced topics. While periodontal disease may not be fully curable, it can be managed with proper care and treatment. If you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your dental health, it is essential to consult a dentist for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.

Recent Comments